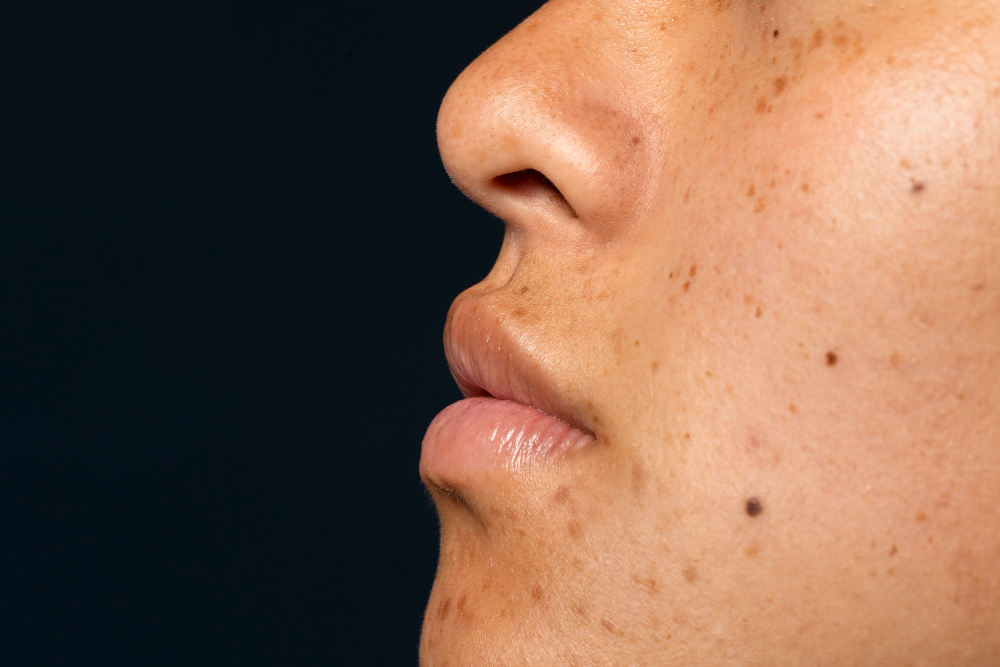
What is Melasma?
Melasma is a common skin condition. It causes brown or gray patches to appear on the face. Often, these patches show up on the cheeks, forehead, nose, or upper lip. Many people notice melasma during sunny months. Because it is harmless, melasma does not cause pain or itching. However, it can affect how you feel about your skin. For many, melasma is a cosmetic concern. Both men and women can get melasma, but it is more common in women. According to the American Academy of Dermatology, melasma affects millions worldwide.
Common Symptoms of Melasma
Melasma symptoms are easy to spot. Usually, you will see:
These patches do not hurt or itch. Still, they may become darker with sun exposure. Because melasma can look like other skin problems, it is important to get the right diagnosis.
Causes and Risk Factors
Doctors are not sure what causes melasma. However, several factors can increase your risk. For example, these include:
Because these factors can work together, it is sometimes hard to know the exact cause. Still, knowing your risks can help you take steps to prevent melasma.
How Melasma is Diagnosed
Doctors usually diagnose melasma by looking at your skin. First, your dermatologist will ask about your medical history. Next, they may use a special light called a Wood’s lamp. This helps them see how deep the pigment is in your skin. Rarely, a skin biopsy may be needed to rule out other conditions. Because melasma can look like other skin problems, it is important to get a professional diagnosis. Early diagnosis can help you start the right treatment.
Treatment Options for Melasma
Melasma treatment options depend on how severe your symptoms are. Some people see improvement without treatment, especially after pregnancy. However, many need help to lighten the patches. Common treatments include:
Because some treatments can irritate the skin, always follow your dermatologist’s advice for melasma. Results may take several months. In some cases, melasma can return, especially with sun exposure.
Lifestyle Tips and Prevention
While melasma is not always preventable, you can lower your risk. Try these tips:
Because sun exposure is a major trigger, daily protection is key. For many, these steps can help prevent melasma or keep it from getting worse.
When to See a Dermatologist
If you notice new dark patches on your skin, it is a good idea to see a dermatologist. Especially if the patches change quickly or do not fade, professional advice is important. A dermatologist can confirm if you have melasma and suggest the best treatment. Early care can improve results and help prevent the patches from spreading. For personalized advice on melasma, always consult a dermatologist.